Section B
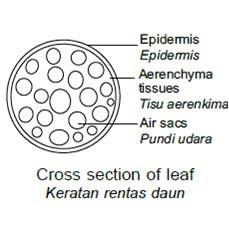
4. (a) Plant X is a floating aquatic plant.
Large air sacs found in roots and leaves keep the plant afloat.
Upward thrust of water supports the plant.
Few vascular tissues in stems enable the stems to bend without breaking.
Plant X has aerenchyma tissues.
Plant Y is a herbaceous plant.
Support is provided by turgidity of parenchyma cells and also by collenchyma and xylem tissues.
Parenchyma cells become turgid when vacuoles are filled with water.
Collenchyma cells have unevenly thickened cellulose walls.
Primary xylem tissues with lignified walls provide support.
(b) (i) Fish swims in water using the caudal fin.
Contraction and relaxation of the antagonistic myotome muscles are found on either side of the fish body brings about lashing of caudal fin from side to side producing forward thrust to propel the fish forward.
(ii) Problems faced by a fish during movement are rolling, yawing and pitching.
Such movements are counteracted by the fins.
Fish has pectoral fins, pelvic fins, dorsal and ventral fins to overcome such problems.
Dorsal fin and ventral fin control rolling of fish.
Dorsal fin and ventral fin control yawing.
Pectoral fins and pelvic fins control pitching which is the vertical displacement in the water.
Pectoral fins allow the fish to swim up and down and to slow down or stop.
5. (a) Movement is brought about by a pair of muscles working in opposing actions.
Extensor muscles contract to straighten the limb.
Flexor muscles contract to bend the limb.
The biceps femoris behind the femur contracts.
At the same time the quadriceps relaxes.
The limb is pulled inwards towards the body and the limb is bent.
When the quadriceps contracts, the biceps femoris relaxes.
The limb is pulled downwards and is straightened .
The quadriceps are extensors whereas the biceps femoris are flexors.
(b) Birds fly in the air.
They need to overcome air resistance. Air provides very little support.
Flight mechanism depends largely on the possession of wings.
Wings act as aerofoils.
Movement of wings creates a flow of air over the wings.
The speed of air is faster on the top of wings.
A higher pressure is created below the wings according to Bernoulli’s principle
A lift force is produced to lift the bird to fly.
Wings are attached to sternum by large powerful muscles.
Contraction of the pectoralis major and relaxation of the pectoralis minor enable the wings to flap downwards; whereas contraction of the pectoralis minor and relaxation of the pectoralis major muscles enable wing to move upwards thus causes the flapping movement of wings.
Streamlined body overcomes air resistance during flight.