3a) Meiosis is a process of cell division producing gametes which are haploid (n) as compared to the parent cell which is diploid (2n).
b)

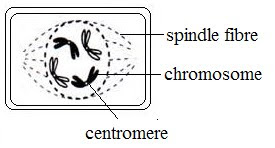
A chromosome consists of 2 chromatids held together at the centromere.
Paring of homologous chromosomes occurs
Crossing over takes place.
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
c)| MITOSIS | MEIOSIS |
| Takes place in somatic cells | Takes place in reproductive cells |
| Produce new cells for growth or tissue repair. | Produce gametes
|
| Involves one division only in one cycle | Involves two divisions in one cycle |
| No pairing of homologous chromosomes | Pairing of homologous chromosomes during Prophase I |
| Crossing over does not occur | Crossing over occurs during Prophase I |
| 2 diploid cells are produced | 4 haploid cells are produced |
| The number of chromosomes in a daughter cell is the same as its parent cell | The number of chromosomes in a daughter cell is the halvedof its parent cell |
| The daughter cells are identical to the parent cell | The daughter cells are not identical to the parent cell and to each other |
4a) Process of cell division is mitosis.
Preparatory stage is interphase.
Interphase

· Replication of DNA
· Storage of energy
· More organelles are produced
· Mitosis consist of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
Prophase
· Chromosomes thicken and shortens
· Each chromosomes consists of 2 chromatids
· Nuclear membrane and nucleolus starts to disappear
Metaphase
· Chromosomes are arranged in a line across the middle of the cell
· Centrosomes are held by spindle fibre
Anaphase· Centromeres of chromosomes divide into 2.
· Chromatids are separated and pulled to the opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase
· Spindle fibres disappear
· Nuclear membrane reappear
· Chromosomes are seen as fine threads
. Formation of cell plates begin
b) Tissue culture can be used to produce more seedlings.
Small pieces of meristem tissue/explant are removed from a parent plant and cut it into small pieces.
Sterilise the pieces of tissues with dilute sodium hypochlorite solution.
Place each sterile tissue onto a culture medium containing nutrients and growth hormone.
The tissue cells are left to divide by mitosis to produce a mass of loosely arranged and undifferentiated cells called callus.
The callus is then stimulated with shoot stimulating hormones to form multiple shoots.
Separate the shoots in nutrient medium with root stimulating hormones to encourage rooting.
Once the roots grow, the plantlets (little plants) are planted in sterile soil to grow into adult plants.